The static keyword is used in java mainly for memory management. It is used with variables, methods, blocks and nested class. It is a keyword that are used for share the same variable or method of a given class. This is used for a constant variable or a method that is the same for every instance of a class. The main method of a class is generally labeled static.
No object needs to be created to use static variable or call static methods, just put the class name before the static variable or method to use them. Static method can not call non-static method.
In java language static keyword can be used for following
- variable (also known as class variable)
- method (also known as class method)
- block
- nested class
Static variable
If any variable we declared as static is known as static variable.
- Static variable is used for fulfill the common requirement. For Example company name of employees,college name of students etc. Name of the college is common for all students.
- The static variable allocate memory only once in class area at the time of class loading.
Advantage of static variable
Using static variable we make our program memory efficient (i.e it saves memory).
When and why we use static variable
Suppose we want to store record of all employee of any company, in this case employee id is unique for every employee but company name is common for all. When we create a static variable as a company name then only once memory is allocated otherwise it allocate a memory space each time for every employee.
Syntax for declare static variable:
public static variableName;
Syntax for declare static method:
public static void methodName() { ....... ....... }
Syntax for access static methods and static variable
Syntax
className.variableName=10; className.methodName();
Example
public static final double PI=3.1415; public static void main(String args[]) { ...... ...... }
Difference between static and final keyword
static keyword always fixed the memory that means that will be located only once in the program where as final keyword always fixed the value that means it makes variable values constant.
Note: As for as real time statement there concern every final variable should be declared the static but there is no compulsion that every static variable declared as final.
Example of static variable.
In the below example College_Name is always same, and it is declared as static.
Static Keyword Example in Java
class Student { int roll_no; String name; static String College_Name="ITM"; } class StaticDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { Student s1=new Student(); s1.roll_no=100; s1.name="abcd"; System.out.println(s1.roll_no); System.out.println(s1.name); System.out.println(Student.College_Name); Student s2=new Student(); s2.roll_no=200; s2.name="zyx"; System.out.println(s2.roll_no); System.out.println(s2.name); System.out.println(Student.College_Name); } }
Example
Output: 100 abcd ITM 200 zyx ITM
In the above example College_Name variable is commonly sharable by both S1 and S2 objects.
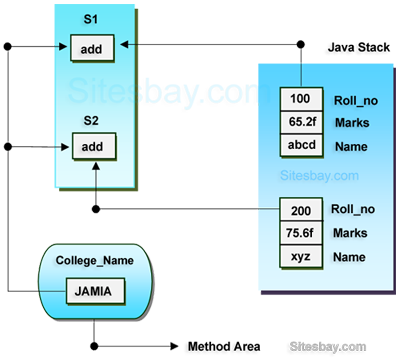
In the above image static data variable are store in method area and non static variable is store in java stack. Read more about this in JVM Architecture chapter
Why Main Method Declared Static ?
Because object is not required to call static method if main() is non-static method, then jvm create object first then call main() method due to that face the problem of extra memory allocation.
Read more about these things in separate
In case of non-static method memory is allocated multiple time whenever method is calling. But memory for static method is allocated only once at the time of class loading. Method of a class can be declared in two different ways
- Non-static methods
- Static methods
Difference between non-static and static Method
| Non-Static method | Static method | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | These method never be preceded by static keyword Example: void fun1() { ...... ...... } | These method always preceded by static keyword Example: static void fun2() { ...... ...... } |
| 2 | Memory is allocated multiple time whenever method is calling. | Memory is allocated only once at the time of class loading. |
| 3 | It is specific to an object so that these are also known as instance method. | These are common to every object so that it is also known as member method or class method. |
| 4 | These methods always access with object reference Syntax:
Objref.methodname();
| These property always access with class reference Syntax:
className.methodname();
|
| 5 | If any method wants to be execute multiple time that can be declare as non static. | If any method wants to be execute only once in the program that can be declare as static . |
Note: In some cases static methods not only can access with class reference but also can access with object reference.
Example of Static and non-Static Method
Example
class A { void fun1() { System.out.println("Hello I am Non-Static"); } static void fun2() { System.out.println("Hello I am Static"); } } class Person { public static void main(String args[]) { A oa=new A(); oa.fun1(); // non static method A.fun2(); // static method } }
Output
Hello I am Non-Static Hello I am Static
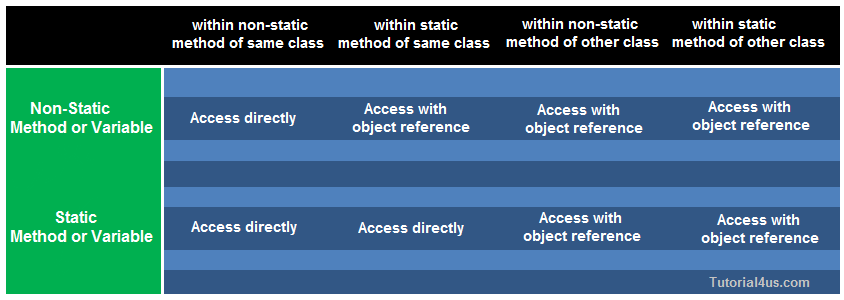
Following table represent how the static and non-static properties are accessed in the different static or non-static method of same class or other class.
Program to accessing static and non-static properties.
Example
class A { int y; void f2() { System.out.println("Hello f2()"); } } class B { int z; void f3() { System.out.println("Hello f3()"); A a1=new A(); a1.f2(); } } class Sdemo { static int x; static void f1() { System.out.println("Hello f1()"); } public static void main(String[] args) { x=10; System.out.println("x="+x); f1(); System.out.println("Hello main"); B b1=new B(); b1.f3(); } }
0 comments:
Post a Comment